Last month I looked at a Functional Web with ASP.NET Core and F#'s Giraffe. Giraffe is F# middleware that takes ASP.NET Core's pipeline in a new direction with a functional perspective. However, Giraffe isn't the only F# web stack to choose from! There's Freya, WebSharper, and there's also a very interesting and quite complete story with The SAFE Stack.
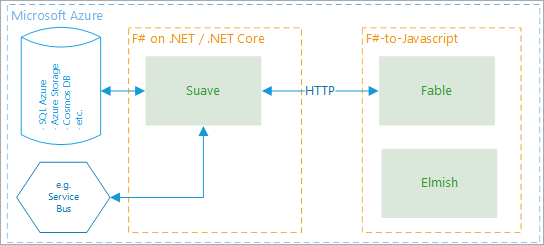
The SAFE Stack is an open source stack, like LAMP, or WAMP, or other acronym stacks, except this one is all open source .NET with a functional perspective. From the announcement blog:
- Suave model for server-side web programming
- Azure for cloud-based systems
- Fable for Javascript-enabled applications.
- Elmish for an easy-to-understand UI programming mode
To be clear, while this is a prescriptive stack, it's not a stack that forces you to do anything. You can swap bits out as you please.
Fable is particularly interesting as it's an F# to JavaScript transpiler. Try Fable online here http://fable.io/repl and turn F# into JavaScript LIVE! Their Sudoku sample is particularly impressive.
Here's two small - but interesting - examples where F# code ends up as JavaScript which ends up creating ReactJS components:
let words size message =
R.span [ Style [ !!("fontSize", size |> sprintf "%dpx") ] ] [ R.str message ]
let buttonLink cssClass onClick elements =
R.a [ ClassName cssClass
OnClick (fun _ -> onClick())
OnTouchStart (fun _ -> onClick())
Style [ !!("cursor", "pointer") ] ] elements
Then later in a Menu.fs that also turns into JavaScript eventually, you can see where they conditionally render the Button for logout, or links for for other Views for the Home Page or Wishlist. You can read lots more about Fable over at the Compositional IT blog.
let view (model:Model) dispatch =
div [ centerStyle "row" ] [
yield viewLink Home "Home"
if model.User <> None then
yield viewLink Page.WishList "Wishlist"
if model.User = None then
yield viewLink Login "Login"
else
yield buttonLink "logout" (fun _ -> dispatch Logout) [ str "Logout" ]
]
Elmish for F# takes the Model View Update (MVU) architecture and brings it to F# and the browser. There's a good breakdown of the value Elmish provides also at the Compositional IT blog.
Suave is its own cross platform Web Server. Here's Hello World in Suave.
open Suave
startWebServer defaultConfig (Successful.OK "Hello World!")
Suave has been around for while and gets better all the time. I blogged about it in 2015 and got it running on Azure. My blog post is not a best practice any more - it was a spike attempt by me - and fortunately they've moved on and improved things.
Here's Suave getting set up within the sample app. Check out how they route HTTP Verbs and URL paths.
let serverConfig =
{ defaultConfig with
logger = Targets.create LogLevel.Debug [|"ServerCode"; "Server" |]
homeFolder = Some clientPath
bindings = [ HttpBinding.create HTTP (IPAddress.Parse "0.0.0.0") port] }
let app =
choose [
GET >=> choose [
path "/" >=> Files.browseFileHome "index.html"
pathRegex @"/(public|js|css|Images)/(.*)\.(css|png|gif|jpg|js|map)" >=> Files.browseHome
path "/api/wishlist/" >=> WishList.getWishList loadFromDb ]
POST >=> choose [
path "/api/users/login" >=> Auth.login
path "/api/wishlist/" >=> WishList.postWishList saveToDb
]
NOT_FOUND "Page not found."
] >=> logWithLevelStructured Logging.Info logger logFormatStructured
startWebServer serverConfig app
Very interesting stuff! There are so many options in .NET open source. I'll be doing podcasts on this stack soon.
Trying out the SAFE Stack
If you're using Visual Studio Community 2017, make sure you've got F# support included. I double-checked under Individual components. You can run the VS2017 installer multiple time and add and remove stuff without breaking things, so don't worry. If you are using other versions of VS, check here http://fsharp.org/use/windows/ to get the right download for your machine. If you're using Visual Studio Code, you'll want the Ionide F# plugin for Code.
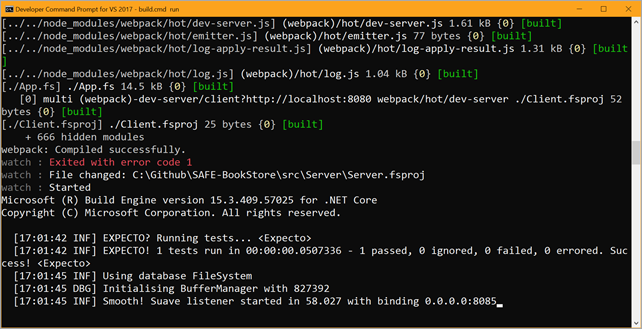
Once I had node and yarn installed, it was easy to try out the sample app and get it running locally with "build run." It uses DotNetWatcher, so you can just keep it running in the background and work on your code and it'll recompile and restart as you go.
The complete "SAFE" stack demo website is LIVE here http://fable-suave.azurewebsites.net (login test/test/) and all the source code for the app is here: https://github.com/SAFE-Stack/SAFE-BookStore.
Sponsor: Do you know how many errors, crashes and performance issues your users are experiencing? Raygun installs in minutes. Discover problems you didn't even know about and replicate bugs with greater speed and accuracy. Learn more!
© 2017 Scott Hanselman. All rights reserved.
from Scott Hanselman's Blog http://feeds.hanselman.com/~/466512192/0/scotthanselman~Learning-about-the-F-SAFE-stack-Suaveio-Azure-Fable-Elmish.aspx
Comments
Post a Comment