 .NET Core is lovely. It's usage is skyrocketing, it's open source, and .NET Core 2.1 has some amazing performance improvements. Just upgrading from 2.0 to 2.1 gave Bing a 34% performance boost.
.NET Core is lovely. It's usage is skyrocketing, it's open source, and .NET Core 2.1 has some amazing performance improvements. Just upgrading from 2.0 to 2.1 gave Bing a 34% performance boost.
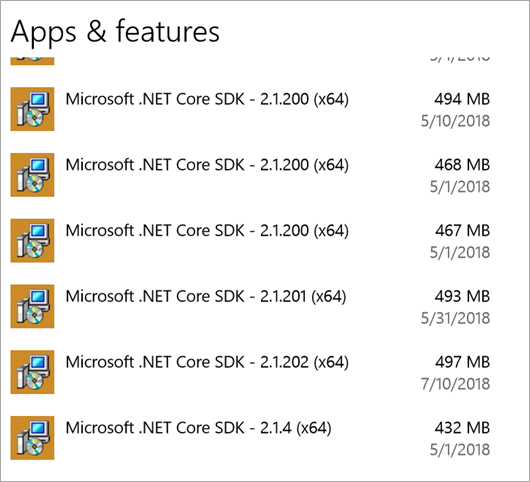
However, for those of us who are installing multiple .NET Core SDKs side by side have noticed that they add-up if you are installing daily builds or very often. As of 2.x, .NET Core doesn't yet have an "uninstall all" or "uninstall all previews" option. There will be work done in .NET Core 3.0 that will mitigate this cumulative effect when you have lots of installers.
If you're taking dailies and it's time to tidy up, the short answer per Damian Edwards is "Delete them all, then nuke the dotnet folder in program files, then install the latest version."
Here's a PowerShell Script you can run on Windows as admin that will aggressively uninstall .NET Core SDKs.
Note the match at the top. Depending on your goals, you might want to change it to "Microsoft .NET Core SDK 2.1" or just "Microsoft .NET Core SDK 2."
Once it's all removed, then add the latest from https://www.microsoft.com/net/download/archives
Here's the script, which is an improvement on Andrew's comment here. You can improve it as it's on GitHub here https://github.com/shanselman/RemoveDotNetCoreSDKInstallers. This scripts currently requires you to hit YES as the MSIs elevate. It doesn't work right then you try /passive as a switch. I'm interesting if you can get a "torch all Core SDK installers and install LTS and Current" script working.
$app = Get-WmiObject -Class Win32_Product | Where-Object {
$_.Name -match "Microsoft .NET Core SDK"
}
Write-Host $app.Name
Write-Host $app.IdentifyingNumber
pushd $env:SYSTEMROOT\System32
$app.identifyingnumber |% { Start-Process msiexec -wait -ArgumentList "/x $_" }
popd
This PowerShell is Windows-only, of course.
If you're on RHEL, Ubuntu/Debian, there are scripts here to try out https://github.com/dotnet/cli/tree/master/scripts/obtain/uninstall
Let me know if this script works for you.
Sponsor: Copy: Rider 2018.2 is here! Publishing to IIS, Docker support in the debugger, built-in spell checking, MacBook Touch Bar support, full C# 7.3 support, advanced Unity support, and more.
© 2018 Scott Hanselman. All rights reserved.
from Scott Hanselman's Blog http://feeds.hanselman.com/~/571134816/0/scotthanselman~Scripts-to-remove-old-NET-Core-SDKs.aspx
Comments
Post a Comment