Thousands of years ago your ancestors, and myself, were using DOS (or CMD) pressing F7 to get this amazing little ASCII box to pop up to pick commands they'd typed before.
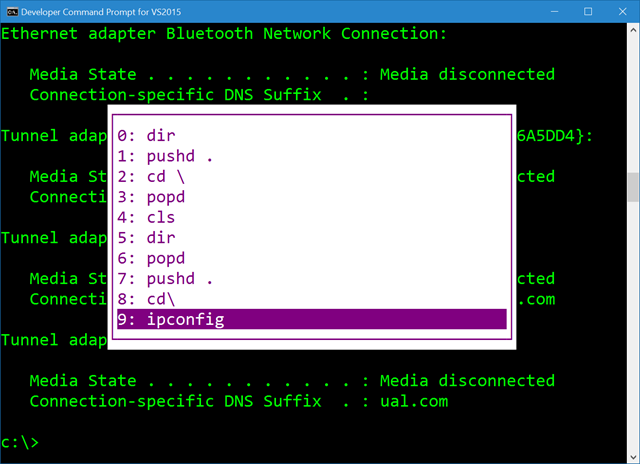
When I find myself in cmd.exe I use F7 a lot. Yes, I also speak *nix and Yes, Ctrl-R is amazing and lovely and you're awesome for knowing it and Yes, it works in PowerShell.

Here's the tragedy. Ctrl-R for a reverse command search works in PowerShell because of a module called PSReadLine. PSReadLine is basically a part of PowerShell now and does dozens of countless little command line editing improvements. It also - not sure why and I'm still learning - unknowingly blocks the glorious F7 hotkey.
If you remove PSReadLine (you can do this safely, it'll just apply to the current session)
Remove-Module -Name PSReadLine
Why, then you get F7 history with a magical ASCII box back in PowerShell. And as we all know, 4k 3D VR be damned, impress me with ASCII if you want a developer's heart.
There is a StackOverflow Answer with a little PowerShell snippet that will popup - wait for it - a graphical list with your command history by calling
Set-PSReadlineKeyHandler -Key F7
And basically rebinding the PSReadlineKeyHandler for F7. PSReadline is brilliant, but I what I really want to do is to tell it to "chill" on F7. I don't want to bind or unbind F7 (it's not bound by default) I just want it passed through.
Until that day, I, and you, can just press Ctrl-R for our reverse history search, or get this sad shadow of an ASCII box by pressing "h." Yes, h is already aliased on your machine to Get-History.
PS C:\Users\scott> h
Id CommandLine
-- -----------
1 dir
2 Remove-Module -Name PSReadLine
Then you can even type "r 1" to "invoke-history" on item 1.
But I will still mourn my lovely ASCII (High ASCII? ANSI? VT100?) history box.
Sponsor: Manage GitHub Pull Requests right from the IDE with the latest JetBrains Rider. An integrated performance profiler on Windows comes to the rescue as well.
© 2018 Scott Hanselman. All rights reserved.
from Scott Hanselman's Blog http://feeds.hanselman.com/~/600072732/0/scotthanselman~F-is-the-greatest-PowerShell-hotkey-that-no-one-uses-any-more-We-must-fix-this.aspx
Comments
Post a Comment